Thread-Safe Stack and Queue Implementation in Python
Using Queue and LifoQueue class from in-built queue module to create Thread-Safe queue and stack in Python
▶️ Thread-Safe Stack Implementation
Stack is a linear data structure storing the elements in Last In First Out (LIFO) manner. This means, the last element added onto the stack will be the first one to be removed. The functions most commonly associated with stack are:
Add/Push element in Stack
Remove/Pop element from Stack
Get top element of Stack
Check if stack is empty or not
Get length of Stack
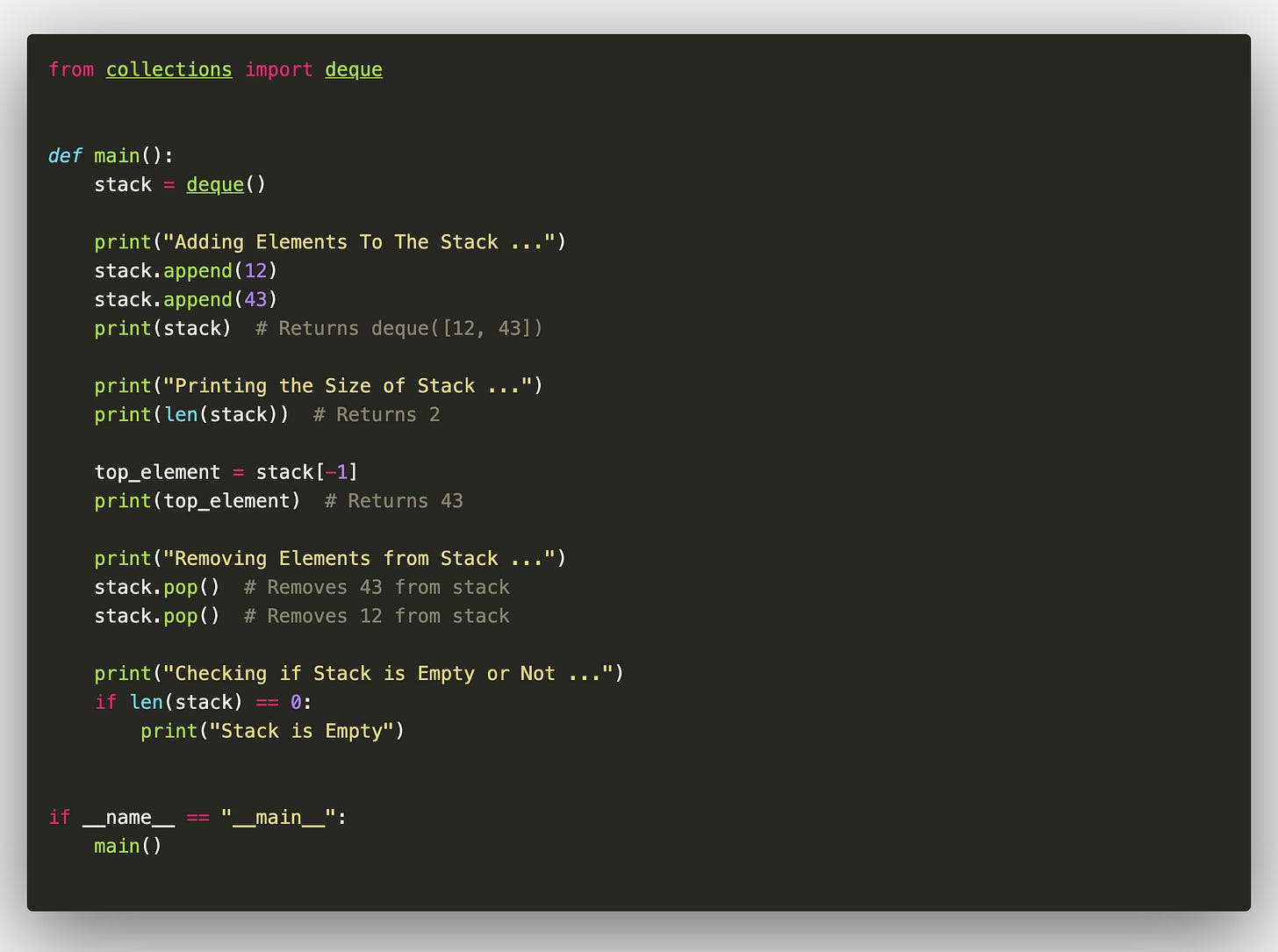
In Python, generally the stack is implemented using either a list or using the deque class from the collections module. Here’s an implementation of all the above functions using the deque class :
Now, the deque class provides an efficient stack implementation with O(1) time complexity for both adding and removing elements from the stack. However, here are some of the problems in above approach:
deque is not inherently thread-safe i.e. if multiple threads are accessing the same deque object simultaneously (without using any locking mechanism), one may encounter race conditions or data corruption. Introducing explicit locking using threading. Explicit locking is possible but it introduces performance overhead due to frequent context switching or lock contention.
deque also doesn’t support size-limited stacks inherently. One needs to manually check and enforce size constraints.
Here is an example that demonstrates the above problem :
Here we created a stack using deque class and had two different threads access it simultaneously - one thread adding 500 values to stack while the other concurrently removing 500 values. So if the implemented stack was thread-safe, the final value should’ve been zero (WHICH IT ISN’T).
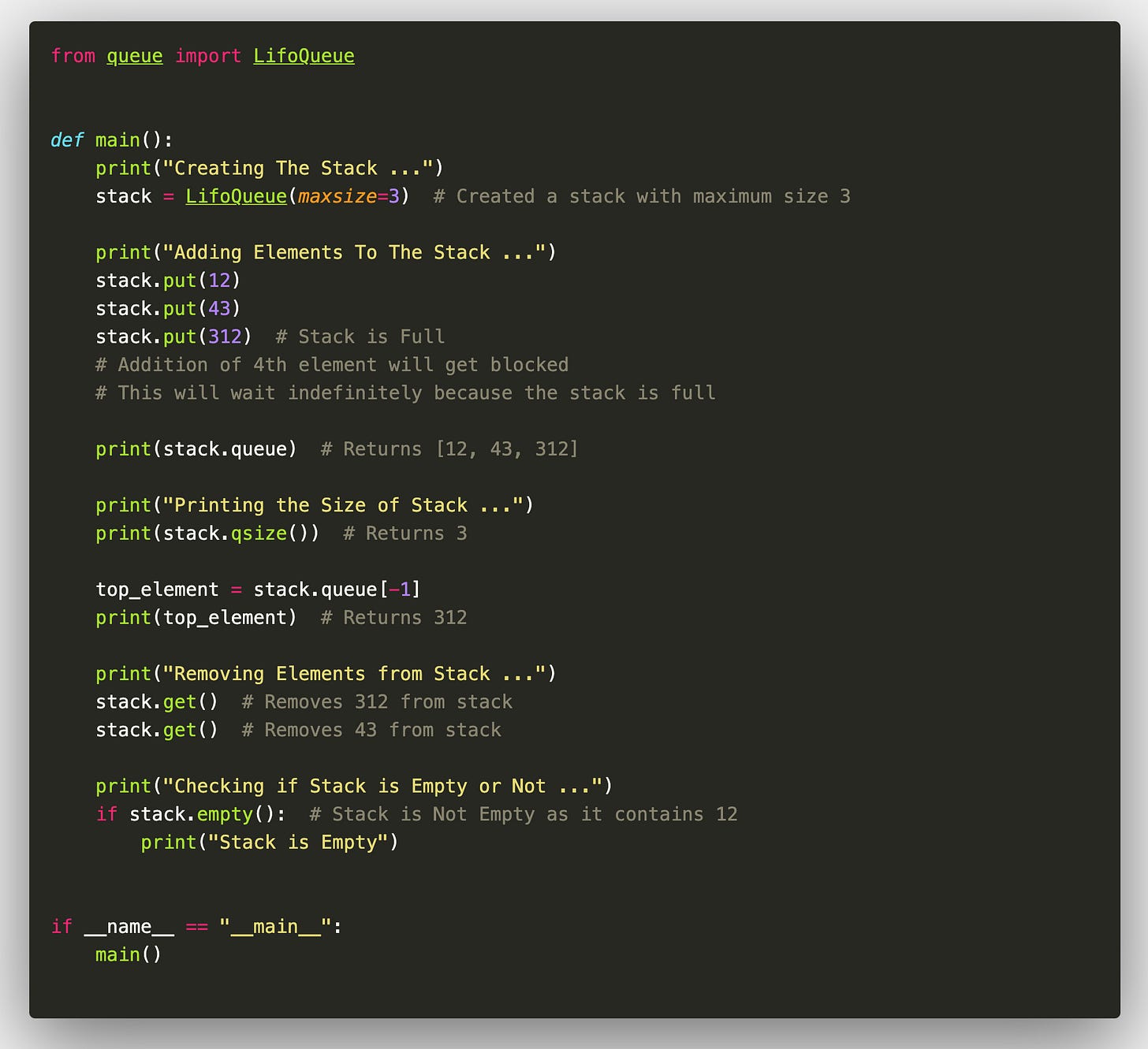
Solution to this issue is LifoQueue from the queue module in python, which provides a thread-safe stack implementation with built-in locking, making it suitable for multi-threaded environments where concurrent access is required.
Here’s the implementation of stack using LifoQueue:
Now, if we run the same multithreaded code as shown above using LifoQueue, it gives the output length of stack to be zero (since it’s thread-safe) :
▶️ Thread-Safe Queue Implementation
Similar to stack, we have the problem in queue also. A queue is a linear data structure that stores elements in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner, meaning the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed.
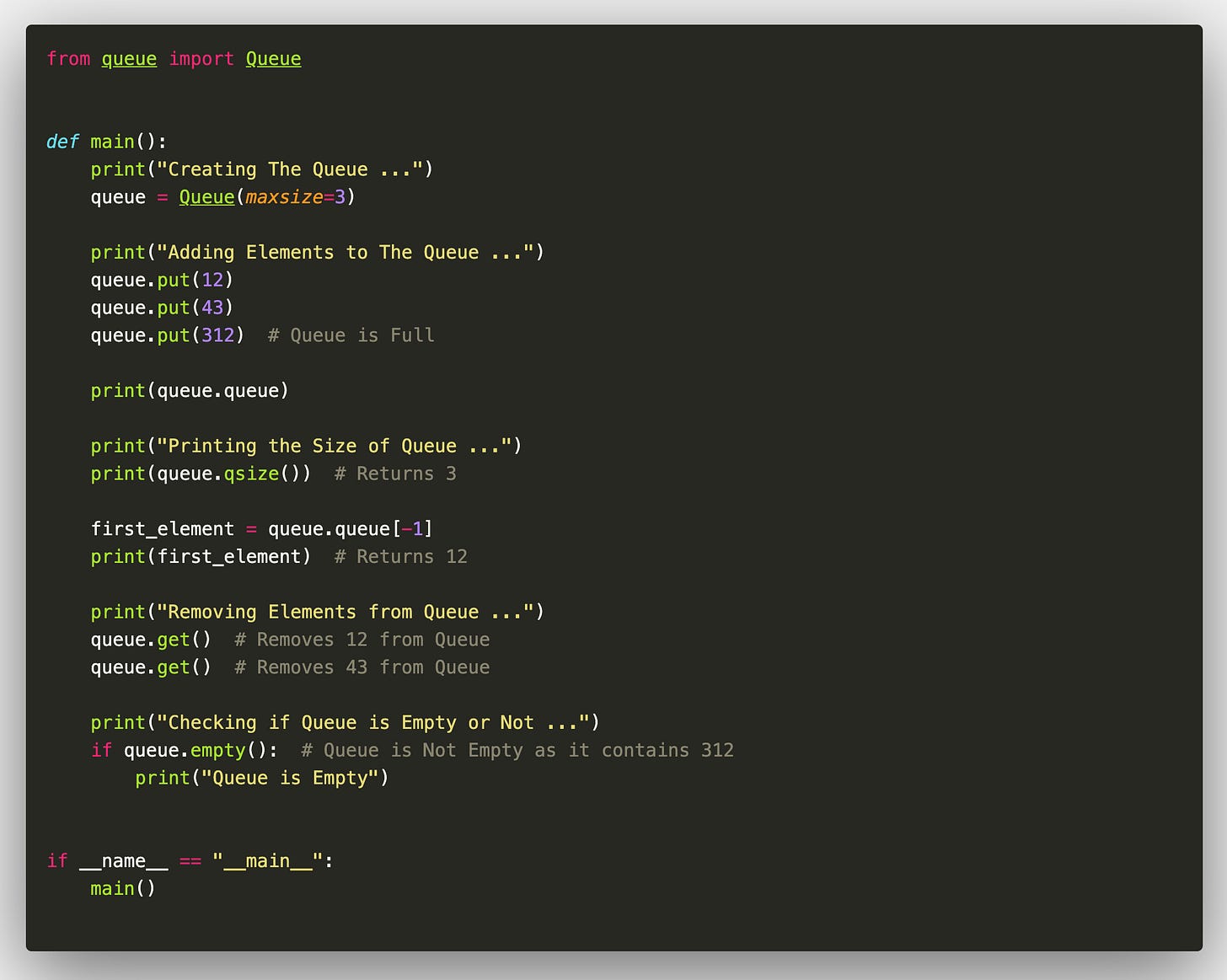
In Python, a queue can also be implemented using either a list or the deque class from the collections module. But as seen in case of stack, these implementations are also not thread safe.
Thus, for queue, we use Queue class from queue module to implement a thread-safe queue. Here’s the implementation of queue using Queue class :
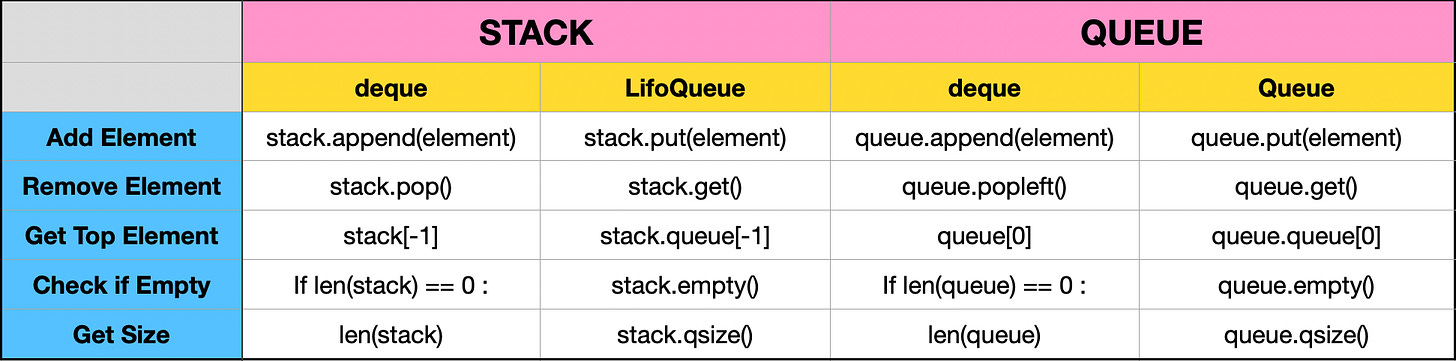
Comparison Table
If we create Stack and Queue by the variable names “stack“ and “queue”, here’s a table showing how the common operations will be done on these two :
Hope this helps!